Not so long ago, we got acquainted with AMD Cezanne desktop processors – hybrid solutions based on the Zen 3 microarchitecture with integrated graphics. And although the graphics cores in them remain exactly the same as in the previous generation of AMD APUs (known under the code name Renoir), the new Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G suddenly turned out to be much more relevant. It’s all about the situation in the video card market, where any available offers are frightening with completely unacceptable prices, and in the category “cheaper than $ 900.” you can only buy obsolete entry-level accelerators.

However, this is not all. The attraction of building a gaming PC based on Cezanne is also that these processors are quite good in terms of computing performance – their power is certainly enough for systems with modern mid-range graphics cards. So, a system based on Ryzen 7 5700G or Ryzen 5 5600G can be a kind of starting configuration for a gamer. While it is not possible to buy a discrete video accelerator, the assembly on one of the Cezanne can be used without graphics. And then, when (if) the graphics cards are available for sale at reasonable prices, it can be turned into a more powerful gaming computer.
How systems based on the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G work with a fast discrete graphics card, we explored earlier. And now we are going to find out how well the integrated graphics in the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G look against the background of the “inexpensive” video cards available for sale for those same $ 450. In other words, we will check whether desktop Cezannes really make offerings like the GeForce GT 1030 or GeForce GTX 1050 Ti pointless. And at the same time, let’s try to squeeze the maximum possible out of the integrated Vega core with the help of overclocking.
But the main question is: does AMD deserve credit for solving the problem of building low-cost gaming PCs in the current realities? Or should you still not look at desktop Cezanne as full-fledged gaming solutions?
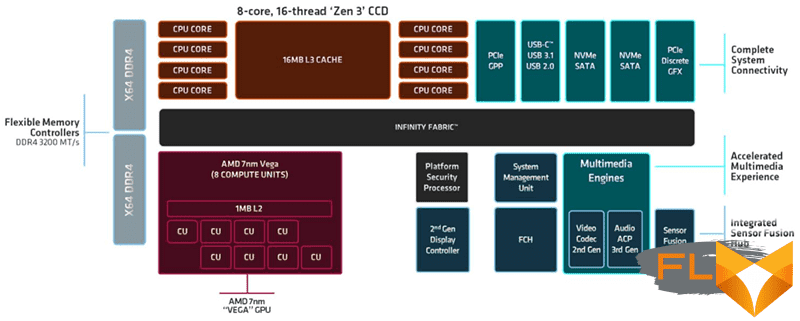
⇡#Cezanne desktop processors in brief
The desktop processors of the Cezanne family hit the market after a noticeable pause – the previous consumer APUs for desktops that AMD officially sold at retail were introduced in 2019, and these were Picassos on the long-standing Zen + architecture. Newer Renoirs with Zen 2 cores have been supplied exclusively to OEM builders, though that hasn’t stopped them from popping up in retail from time to time. But the new Cezannes, like the Picassos, are aimed specifically at individual users, and this is a logical step for AMD in a world in which video cards are a scarce commodity.
It should be said right away that no radical changes have taken place in the graphic part of Cezanne. Compared to Picasso, the architecture of the graphics core has been noticeably improved, but compared to Renoir – practically not. Nevertheless, the use of a mature 7nm process technology allowed AMD not only to significantly increase the frequencies of the integrated GPU, but also leave a significant margin that can be unlocked by overclocking. It is thanks to this that the graphics in Cezanne look better than in previous generations of hybrid processors.
The Cezanne desktop family includes three representatives with eight, six and four Zen 3 cores. This assumes that the quad-core Ryzen 3 processor should only be available as part of finished computers, while representatives of the Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 series are sold in stores as in a boxed (with Wraith Stealth cooler) and non-boxed configuration.
| Cores/Threads | Basic/max. frequency, GHz | L3 cache, MB | GPU | GPU frequency, GHz | TDP, W | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 7 5700G | 8/16 | 3.8/4.6 | 16 | Vega 8 | 2.0 | 65 | $359 |
| Ryzen 5 5600G | 6/12 | 3.9/4.4 | 16 | Vega 7 | 1,9 | 65 | $259 |
| Ryzen 3 5300G | 4/8 | 4.0/4.2 | 8 | Vega 6 | 1.7 | 65 | – |
Given the market situation, the recommended prices installed on the Ryzen 5000G processors can even be called democratic. And it’s not just that Cezannes cost less than most video cards, they can be bought cheaper than “full-fledged” Ryzen 5000 processors with the same number of cores. True, as we saw earlier, hybrid Cezannes are quite noticeably inferior to them in performance, despite the fact that they are built on the basis of the same Zen 3 microarchitecture.
It turns out this is due to the fact that Cezanne are much closer relatives of mobile than desktop processors of the Ryzen 5000 series, and this is what defines their features. The Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G are based on exactly the same single monolithic 7nm semiconductor die as in the respective laptop solutions. Moreover, the foundations of the Cezanne topology were laid back in the last generation of Renoir mobile processors – since then, the processor cores have changed in the chip, but the elements of the north bridge, integrated Vega graphics and the overall design of the SoC have remained unchanged.
As a result, the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G use the same Vega graphics core with eight or seven compute units as the Renoir processors. Architecturally, this core takes us back four years, and for some reason the more modern RDNA graphics architecture did not make it into Cezanne. Moreover, the Vega 8 core in the Ryzen 7 5700G is clocked down by 100 MHz when compared to the Ryzen 7 Pro 4750G, but the Vega 7 graphics in the Ryzen 5 5600G still run at the same frequency as the Ryzen 5 Pro 4650G. Nevertheless, we would not advise you to seriously think about AMD’s hybrid chips of the past generation. Along with Vega graphics, they are equipped with computing cores with the previous generation of microarchitecture – Zen 2, the performance of which may not be enough after installing a discrete graphics accelerator in the system.
However, when a discrete graphics card gets into a Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G based computer, they still don’t perform as well as the Ryzen 7 5800X and Ryzen 5 5600X. It’s all about solidity: by assembling Cezanne on a single semiconductor chip, AMD was unable to accommodate the same amount of cache memory in it as in processors without an integrated GPU. As a result, the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G only have 16 MB of L3 cache, while the non-graphics Ryzen 5000 series has twice the cache. But on the other hand, the cache in Cezanne is twice as large as in Renoir, in addition, as in all desktop processors with Zen 3 cores, the L3 cache in Cezanne is single, and not divided into two halves – one for each quartet (or triple) of cores . This not only increases the efficiency of such a cache, but also reduces inter-core communication delays, which makes the performance gap between the new Cezanne and the previous Renoir even more significant.
It is noteworthy that in even older Picasso generation hybrid processors, the integrated Vega graphics core could contain up to 11 computing devices. Now the graphics have become clearly simpler. But AMD says that the new versions of Vega are still noticeably faster, thanks to both architecture optimizations and a significant boost in GPU frequency provided by 7nm technology. In other words, the absence of obvious breakthroughs in the graphics direction does not mean that Cezanne has any alternatives – as an entry-level gaming PC solution, these processors are better suited than others.
⇡#Vega graphics core overclocking
Processors with integrated graphics, of course, are not intended for games in 4K resolution at maximum quality settings. They want to get acceptable performance in 1080p. Initial testing of the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G showed that there are no particular problems with this, but in many modern games you will have to focus on low graphics quality. If you want to see a better picture, you have to sacrifice image clarity and go to 720p.
In general, similar words could be said about entry-level video cards, especially those equipped with 2 GB of memory, which is no longer enough for many modern games. The Vega core embedded in Cezanne processors is free from this shortcoming – it can dynamically capture the required amount of system memory. However, compared to the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, Vega’s chances don’t seem that high: for example, the video memory of this discrete graphics card has a bandwidth of 112 GB / s, while dual-channel DDR4-3200 in a system with Cezanne processors gives only 51 GB / s .
However, no one forbids trying to fight – the Vega core overclocks well, and its frequency can be raised much higher than 2.0 GHz, plus a noticeable increase in the performance of the integrated graphics can give an increase in the frequency of the system memory – and here systems with Cezanne processors also have something to brag about.
In general, the overclocking of the Vega graphics core in the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors follows a completely standard algorithm: the supply voltage and frequency increase. Both of these settings can be changed independently in the motherboard BIOS. In addition, you should not lose sight of the voltage on the SoC – it should not be lower than the voltage on the GPU, since the second is formed on the basis of the first. The maximum level of these voltages, which seems safe, according to everyone’s belief, is 1.3 V, and this is enough for a fairly noticeable increase in frequency.
So, by setting the SoC and GPU voltage to 1.25 V, we managed to achieve stable graphics operation at a frequency of 2.5 GHz for the Ryzen 7 5700G processor and 2.4 GHz for the Ryzen 5 5600G processor. In both cases, the increase was 500 MHz, or 25%, a significant result.
 |  |
As we saw in previous tests, the performance of integrated graphics is strongly affected not only by its frequency, but also by the speed of the memory, which is natural, since the graphics use the same system memory as the computing cores. In addition, the frequency of the Infinity Fabric bus, which in Ryzen processors brings together all the processor components, is directly related to the memory frequency. Although Cezanne is a single-chip processor, the Infinity Fabric bus is also used in it, and it provides communication between the GPU and the memory controller.
It is well known that when overclocking Ryzen processors, it is more rational to use synchronous mode, when the memory, memory controller and Infinity Fabric operate at the same frequency. The same recommendation should be followed if we are talking about Cezanne – here synchronous operation is even more important, since it eliminates unnecessary delays on the highway from the GPU to the memory.
With familiar Ryzen 5000 processors without integrated graphics, motherboards by default use synchronous frequencies up to DDR4-3600 mode, activating a 1: 2 divider for its controller at higher memory speeds and freezing the FCLK frequency at around 1800 MHz. With Ryzen 5000G processors, things are a little different. They use not one 128-bit, but two 64-bit memory controllers, which are also compatible not only with DDR4, but also with LPDDR4X memory. The latter feature is needed for mobile versions of Cezanne, however, in relation to desktop systems, it is converted into the possibility of synchronous operation of memory controllers with faster DDR4 SDRAM modules.
By default, Socket AM4 boards, when Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors are installed in them, use synchronous clocking of memory controllers up to and including DDR4-4000 mode, but for higher DDR4 frequencies, the FCLK speed is fixed at 2000 MHz and switched to a half divider memory controller frequencies. However, this does not mean that memory overclocking in synchronous mode beyond DDR4-4000 is impossible. Unlike regular Ryzen 5000s, the Ryzen 5000G series can use synchronous mode for much higher memory frequencies. It just needs to be configured manually.
All this is configured in a quite obvious way – manually setting the FCLK frequency to half the effective frequency of DDR4 memory. For example, when overclocking memory to DDR4-4200, the FCLK frequency for synchronous mode should be set to 2100 MHz, and for DDR4-4800 – to 2400 MHz. Cezanne, oddly enough, is able to work even with these settings, but it is necessary that the memory modules used in the system can take such frequencies. It is for this reason that overclocking high-frequency memory sticks based on Samsung B-die chips are a reasonable choice for systems with Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors. The only thing that may be additionally required to ensure the stability of these processors when working with high-speed memory in synchronous mode is an increase in the SoC voltage to 1.25-1.3 V.
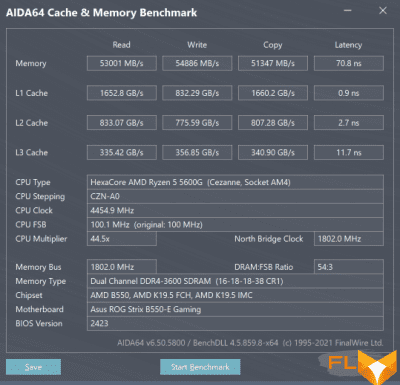
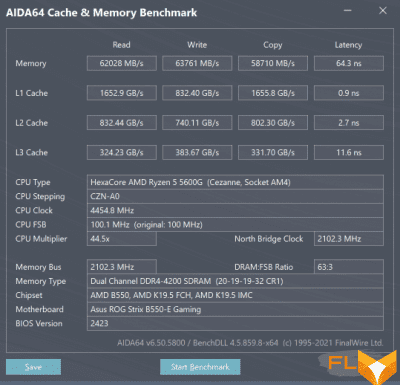
However, practice shows that not all motherboards are suitable for significant FCLK overclocking. So, the ASUS ROG STRIX B550-E GAMING board we used in testing, unfortunately, for some reason, limits the possibility of increasing the FCLK frequency at around 2100 MHz, when passing through which the system simply stops starting. Therefore, in our case, memory overclocking had to be limited to DDR4-4200 mode, which, however, with the dual-rank 16 GB Crucial Ballistix DDR4-3600 modules we use on Micron Rev.E chips (Crucial Ballistix RGB BL2K16G36C16U4BL) is even better, since it allows not too relax timings and use the 20-19-19-19-32 scheme. The theoretical memory bandwidth in this case increases to 67.2 GB / s. The values of the practically measured characteristics of the memory subsystem are shown in the AIDA64 Cachemem screenshot below. Next to the screenshot taken in the DDR4-4200 mode, for comparison, there are similar indicators for the DDR4-3600 mode with XMP delay configuration.
| DDR4-3600, 16-18-18-38 | DDR4-4200, 20-19-19-32 |
Such overclocking of the integrated GPU together with the memory allows to increase graphics performance by about a quarter, judging by the results of 3DMark Time Spy.
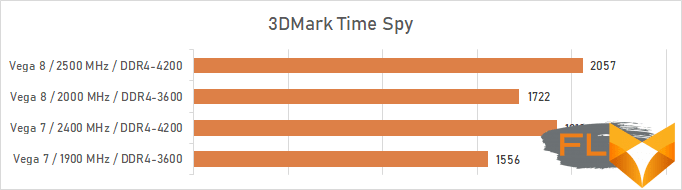
This allows us to hope that the Vega graphics in the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G can be seriously considered as an entry-level gaming accelerator, and we will check this assumption further.
⇡#Description of test systems
The goal of testing indicated at the beginning of the material is to determine the performance of the Vega 8 and Vega 7 graphics cores built into the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors in a coordinate system tied to the speed of entry-level graphics cards. Only two relatively inexpensive accelerators are currently available in stores: GeForce GT 1030 and GeForce GTX 1050 Ti – both of them will serve as rivals for Vega. In addition, the Radeon RX 550 4 GB video card also took part in the tests – we included it in the tests as an addition to the GeForce GT 1030, the performance of which is limited by 2 GB of video memory.
- Processors:
- AMD Ryzen 7 5700G (Cezanne, 8 cores + SMT, 3.8-4.6GHz, 16MB L3);
- AMD Ryzen 5 5600G (Cezanne, 6 cores + SMT, 3.9-4.4GHz, 16MB L3).
- CPU cooler: EKWB custom coolant
- Motherboard: ASUS ROG Strix B550-E Gaming (Socket AM4, AMD B550).
- Memory: 2 × 16GB DDR4-3600 SDRAM, 16-18-18-38 (Crucial Ballistix RGB BL2K16G36C16U4BL).
- Video cards:
- ASUS GeForce GT 1030 LP (GP108, 1228-1506/6000MHz, 2GB GDDR5 64-bit);
- MSI GeForce GTX 1050 Ti 4G OC (GP107, 1341-1455/7008MHz, 4GB GDDR5 128-bit);
- PowerColor Red Dragon RX 550 4GB GDDR5 (Lexa, 1071/6000MHz, 4GB GDDR5 64-bit).
- Disk subsystem: Intel SSD 760p 2TB (SSDPEKKW020T8X1).
- Power supply: Thermaltake Toughpower DPS G RGB 1000W Titanium (80 Plus Titanium, 1000W).
Testing was performed on the Microsoft Windows 10 Pro (21H1) Build 19042.572 operating system using the following driver set:
- AMD Chipset Software 3.8.17.735;
- AMD Radeon Software Adrenalin 2020 Edition 21.10.3;
- Intel Chipset Driver 10.1.31.2;
- Intel Graphics Driver 3.11.1.0;
- NVIDIA Game Ready Driver 496.49
Integrated graphics Vega 7 and 8 were tested in two modes. At face value – without overclocking and with DDR4-3600. And in overclocking – with an increase in GPU frequency to 2.5 (for Ryzen 7 5700G) or 2.4 GHz (for Ryzen 5 5600G) and with memory in DDR4-4200 mode. Discrete graphics results were filmed on a system based on the Ryzen 5 5600G processor.
⇡#Performance at 720p
As we already know from previous tests, if we are talking about modern AAA games, then when choosing the Full HD resolution, the integrated Vega graphics are enough to provide an acceptable FPS level only at low quality settings. Moreover, even with these assumptions, the frame rate is about 30-40 FPS, which is perceived by many as insufficiently smooth gameplay. Therefore, those users who strive for higher frame rates and better picture quality will have to be content with a resolution lowered to 720p. Yes, clarity suffers from this, but otherwise a high level of FPS will not be achieved.
For tests at this resolution, we used the following games and settings:
- Assassin’s Creed Valhalla. Resolution 1280×720, quality profile Medium.
- Dota 2. 1280×720 resolution, Ultra quality profile.
- Far Cry 6. 1280×720 resolution, High quality profile.
- Fortnite. Resolution 1280×720, quality settings profile High.
- GTA V. 1280×720 resolution, DirectX 11, Ultra High quality profile.
- Horizon Zero Dawn. 1280×720 resolution, Original quality profile.
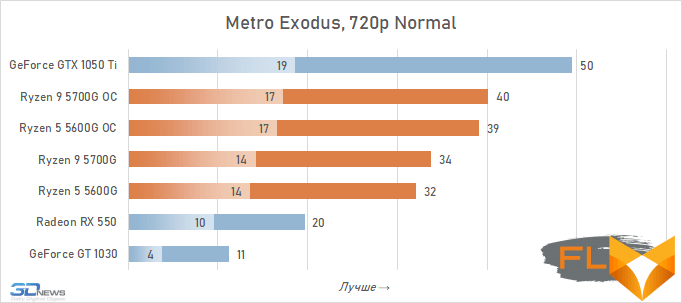
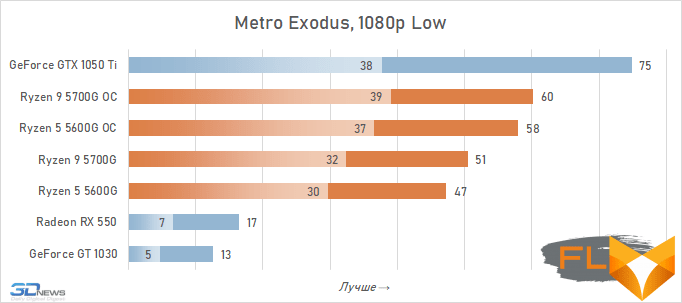
- Metro Exodus. Resolution 1280×720, DirectX 12, Normal quality profile.
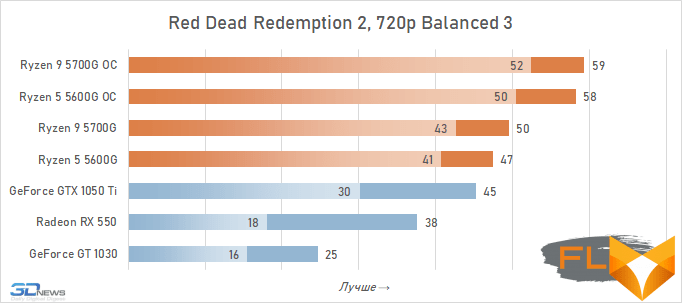
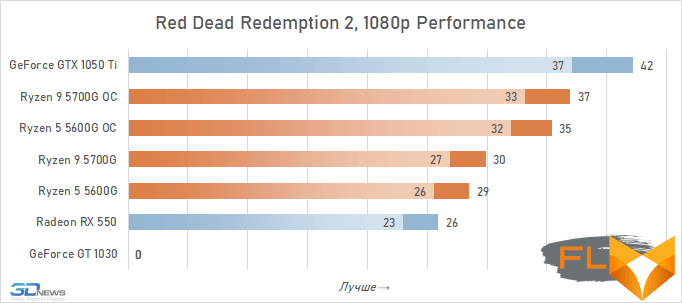
- Red Dead Redemption 2. 1280×720 resolution, Balanced 3 quality profile.
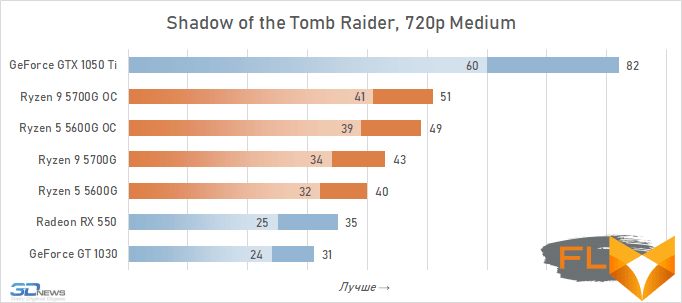
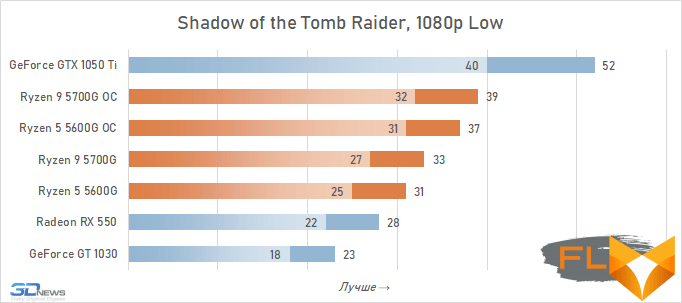
- Shadow of the Tomb Rider. Resolution 1280×720, DirectX12, Medium quality profile.
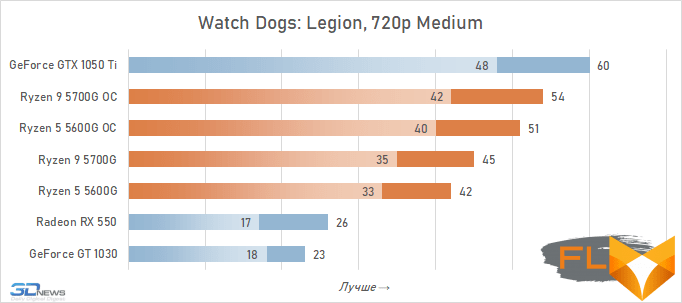
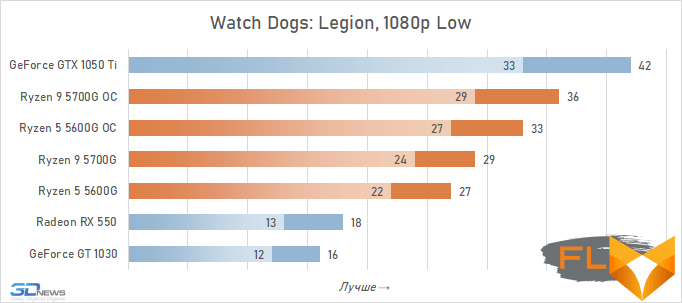
- Watch Dogs: Legion. Resolution 1280×720, quality profile Medium.
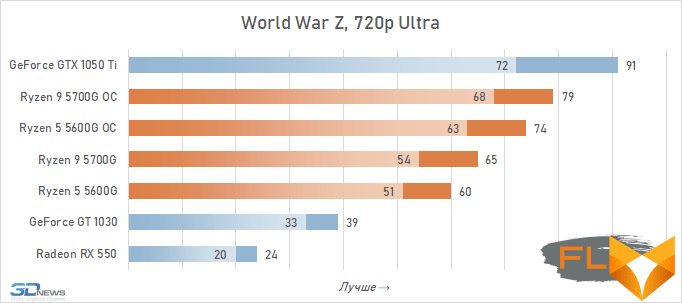
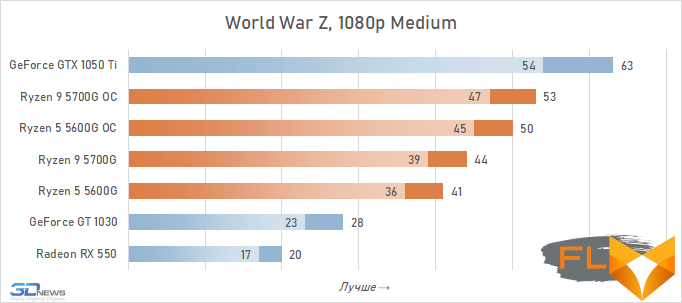
- World War Z. 1280×720 resolution, Vulkan, Ultra quality profile.
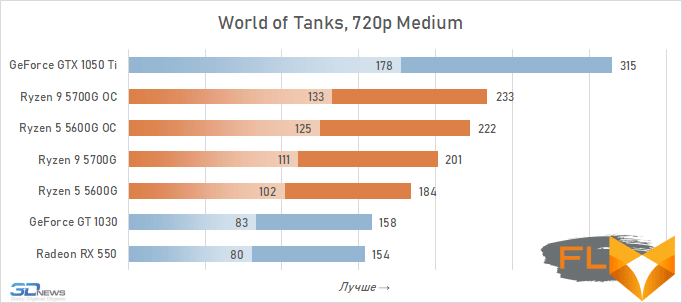
- World of Tanks. Resolution 1280×720, quality profile Medium.
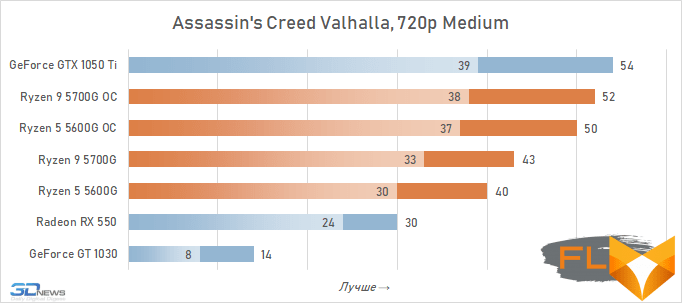
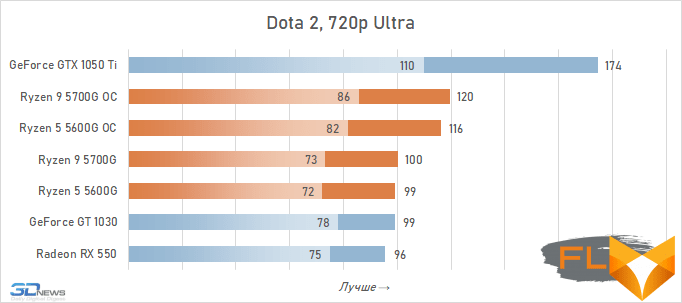
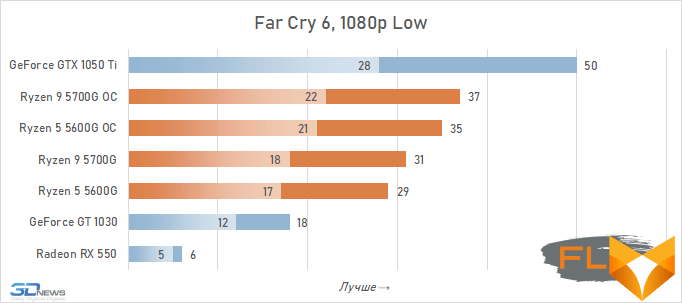
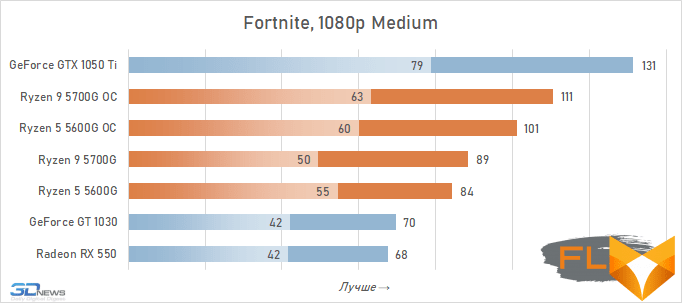
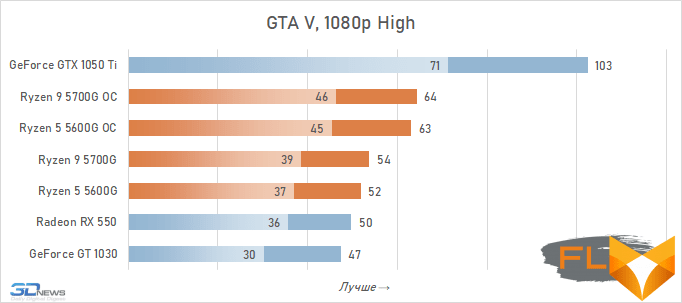
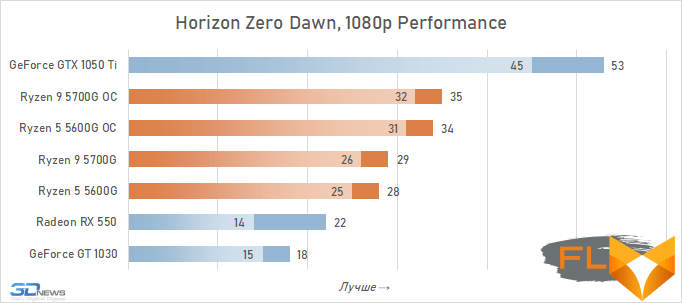
In general, we can state that the integrated Vega graphics cope with the tasks assigned to it. Even in the most demanding games, it can deliver a good level of FPS with at least average image quality. At the same time, the Vega 7 and 8 variants built into the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors, respectively, do not differ so much in performance – the relative gap is about 6%. In addition, overclocking reduces it a bit – the average performance difference is reduced to 4.5%. At the same time, increasing the frequencies of the integrated GPU and memory in both cases leads to a very noticeable result – the frame rate increases by 19-21%.
The fact that the GeForce GT 1030 cannot compete with the graphics core of the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors, we said earlier. Now the same can be said about the Radeon RX 550. Double the amount of video memory (4 GB) compared to the GeForce GT 1030 does not save this video card from defeat.
But with the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, the picture is different. This video card has a twice as wide memory bus and twice as powerful a GPU, and the integrated cores of Vega 7 and 8 can no longer successfully withstand it. Even when overclocked, Vega integrated graphics lag behind by an average of 20-25%. However, the picture for different games is not entirely uniform. The advantage of the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti is higher in older and more graphically simpler titles, while in more modern games the gap is reduced to 10-12%, and in some cases to smaller values. For example, in Assassin’s Creed Valhalla, the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G processors come close to the results of a discrete video accelerator with a current price of over $450, and in Red Dead Redemption 2 they completely outperform not only the GeForce GT 1030, but also the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti.
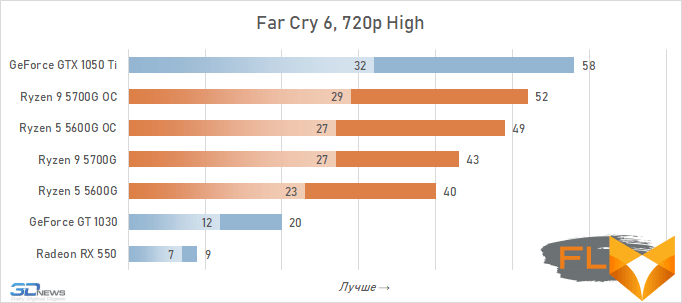
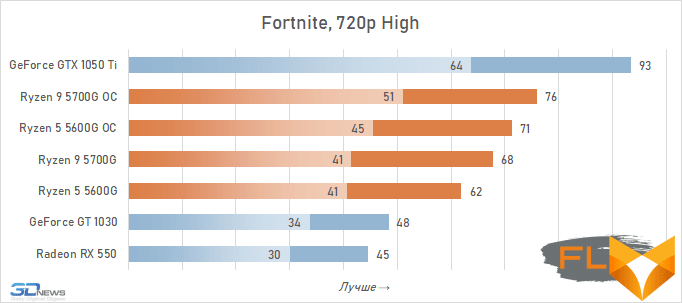
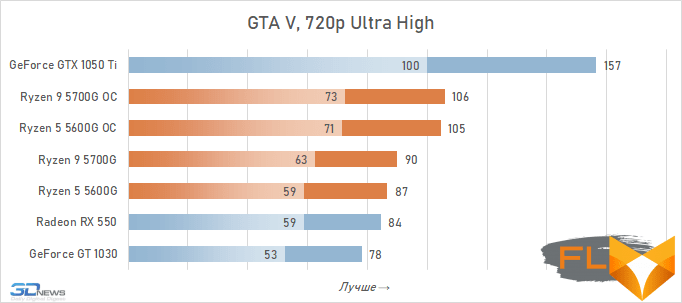
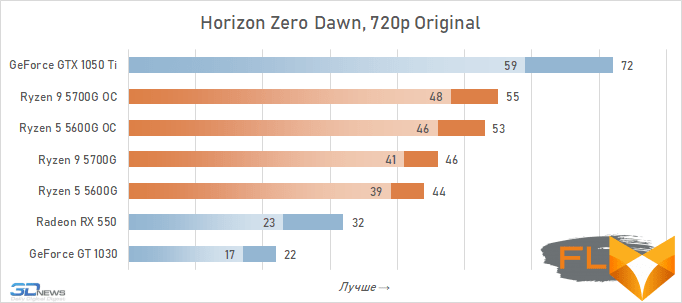
⇡#Performance at 1080p
Increasing the resolution to full HD results in the need to reduce the quality in systems with any weak GPUs. The integrated Vega 7 and Vega 8 are no exception, but it’s fair to say that we couldn’t find a single game where 1080p was completely unplayable on AMD’s integrated graphics. Moreover, in the list of games there were also those where, when switching to this resolution, it was not necessary to lower the quality to the lowest possible – a satisfactory frame rate was achieved even at medium settings.
The list of games and installations in them is given below:
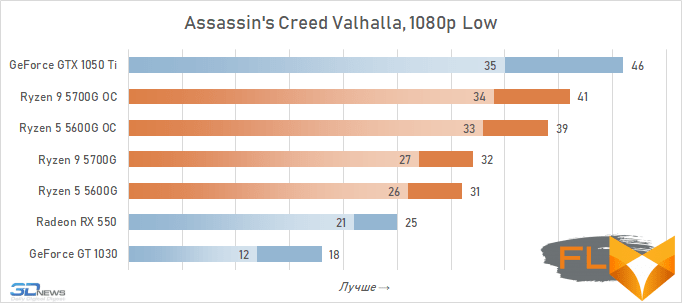
- Assassin’s Creed Valhalla. 1920×1080 resolution, Low quality profile.
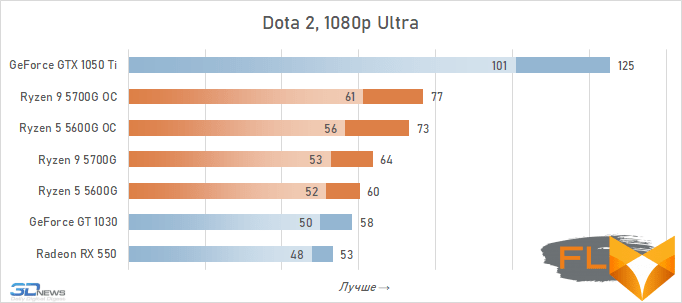
- Dota 2. 1920×1080 resolution, Ultra quality profile.
- Far Cry 6. 1920×1080 resolution, Low quality profile.
- Fortnite. Resolution 1920×1080, quality profile Medium.
- GTA V. 1920×1080 resolution, DirectX 11, High quality profile.
- Horizon Zero Dawn. Resolution 1920×1080, Favor Performance quality settings profile.
- Metro Exodus. 1920×1080 resolution, DirectX 12, Low quality profile.
- Red Dead Redemption 2. 1920×1080 resolution, Favor Performance quality settings profile.
- Shadow of the Tomb Rider. 1920×1080 resolution, DirectX12, Low quality profile.
- Watch Dogs: Legion. 1920×1080 resolution, Low quality profile.
- World War Z. 1920×1080 resolution, Vulkan, Medium quality profile.
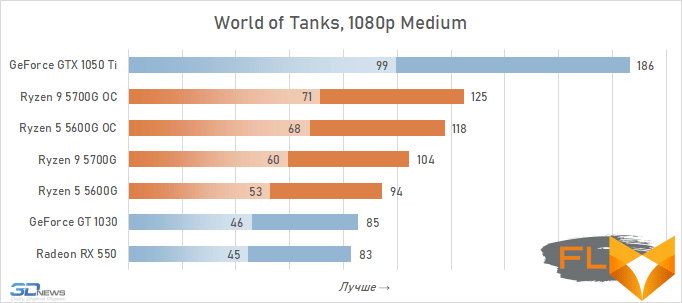
- World of Tanks. Resolution 1920×1080, quality profile Medium.
In general, the test results in 1080p turned out to be almost the same as in 720p – there were no fundamental changes in the relative results when changing the resolution. The difference in the performance of the graphics built into the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G was already the usual 5-7%, about the same gap in the results persists during overclocking. Overclocking itself allows you to increase the frame rate in games by about 20% – and this is also quite expected.
Video cards, the cost of which in current realities is below the conditional mark of $ 300, lose to integrated Vega graphics both with and without overclocking. But the $450 GeForce GTX 1050 Ti already seems like an unattainable rival for Vega. Its average advantage is 30%, which is more than in the case of 720p resolution. This confirms the thesis formulated above that the simpler the game in terms of graphics (the worse the image quality), the stronger the gap between NVIDIA’s discrete accelerator. Even in Assassin’s Creed Valhalla and Red Dead Redemption 2, which favor integrated graphics, the advantage of the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti over the overclocked Vega 8 this time is about 15%. And in games like World of Tanks, GTA V or Dota 2 that do not use modern APIs, integrated graphics can lag behind the GTX 1050 Ti by more than one and a half times even when overclocked to the limit.
But on the other hand, the superiority of the Vega integrated graphics over the GeForce GT 1030 is more than convincing – in demanding games, the AMD solution is about 50% faster even without any overclocking. Moreover, unlike a discrete video accelerator, it never suffers from a lack of video memory – the integrated graphics core is capable of capturing up to 16 GB of system memory if necessary.
In other words, the Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G are intermediate between the GeForce GT 1030 and GeForce GTX 1050 Ti here. Which is very good, if we do not forget that we are talking about productive multi-core processors, in which integrated graphics are by no means the main part.
⇡#Conclusions
Some detailed explanations of how profitable the new AMD processors with integrated graphics look are hardly needed. First, everything is clearly visible in the diagrams above. And secondly, desktop Cezanne came to the market at such a good time that it hardly makes sense to talk about their pros and cons. They represent almost the only option for building an inexpensive gaming system, which can later be turned into a full-fledged high-performance gaming PC.
For the record, it’s worth noting that AMD didn’t really need much innovation to release the Cezanne. These processors are assembled from proven components – Zen 3 compute cores, which have been used in the Ryzen 5000 processors for a year, and the Vega graphics core, transferred from Renoir even without any special changes. Therefore, Ryzen 7 5700G and Ryzen 5 5600G can hardly be classified as technological breakthroughs. These are rather evolutionary proposals that have become especially attractive due to the current market situation.
But all this does not mean at all that we have any specific claims to the new AMD hybrid processors as the basis of an entry-level gaming system. Their integrated Vega graphics are the most powerful graphics core currently found in desktop processors. Its power is enough to provide an acceptable level of FPS in modern games at 1080p resolution with low quality, and at 720p even with medium image quality. And what’s more, in terms of performance, integrated Vega graphics are definitely better than discrete graphics cards in the lower price range (with a recommended price of less than $100).

True, as tests have shown, the integrated Vega core still does not reach the level of the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, even if overclocking is used. But firstly, in some games with complex graphics, the gap between the integrated Vega graphics and the GTX 1050 Ti is not so noticeable. And secondly, this discrete graphics card costs more than the Ryzen 5 5600G. At the same time, for its functioning, it will also require the purchase of a modern processor, but this configuration option will not have any fundamental advantages – the quality in demanding games will have to be reduced with the GTX 1050 Ti.
In other words, thanks to the appearance of desktop Cezanne, the strategy of buying a computer based on an hybrid processor with integrated graphics with an eye to its subsequent modernization with the installation of a high-performance video card has become not only feasible, but completely justified. And here, perhaps, closer attention should be paid to the six-core Ryzen 5 5600G, which costs several hundred dollars cheaper than its older eight-core counterpart, but at the same time offers a similar level of gaming performance of the graphics core and a sufficient level of computational performance to then easily pull out and mid-range discrete graphics card.
FAQ Ryzen 5 5600g as graphics card alternative
How does AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600G APU perform in benchmarks compared to a discrete GPU?
In benchmarks, AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600G APU performs well for an integrated GPU, particularly with its Radeon Vega 7 graphics. However, it may not match the performance of a discrete GPU like an NVIDIA GeForce RTX or GTX series in demanding gaming scenarios.
What are the benefits of the PCIe 4.0 compatibility in the Ryzen 5 3600?
The Ryzen 5 3600’s compatibility with PCIe 4.0 offers faster data transfer rates, especially beneficial for high-speed NVMe SSDs, enhancing overall system performance and reducing load times in applications and games.
Can the integrated Radeon RX Vega graphics in the Ryzen 5 5600G CPU provide a good gaming experience?
The integrated Radeon RX Vega graphics in the Ryzen 5 5600G can provide a decent gaming experience for budget PCs, especially in less graphically demanding games, though it may not match the performance of dedicated GPUs.
How does the AMD Ryzen 5 5600G APU compare to Nvidia GeForce GTX series GPUs?
The AMD Ryzen 5 5600G APU, with its integrated Radeon Vega 7 graphics, offers respectable performance for an integrated GPU but generally falls short of the performance level of dedicated Nvidia GeForce GTX series GPUs.
Is it possible to upgrade to a dedicated GPU later when using a Ryzen 5 5600G with integrated graphics?
Yes, it is possible to upgrade to a dedicated GPU later when using a Ryzen 5 5600G. The APU’s integrated graphics allow for initial use without a discrete GPU, and you can add a dedicated GPU for a performance boost in gaming or graphic-intensive tasks.
What kind of PSU should be used for a system with AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600G and a potential discrete GPU upgrade?
For a system with AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600G and a potential discrete GPU upgrade, a PSU with sufficient wattage to support both the APU and the chosen dedicated GPU is recommended, usually ranging from 500W to 650W depending on the GPU.
How does AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600G fare in terms of CPU cores and graphics processing compared to traditional CPUs?
AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600G comes with 6 CPU cores and Radeon Vega 7 integrated graphics, making it a versatile choice for both general computing and moderate gaming, offering a balance of CPU and GPU performance.
Can the Vega 7 integrated graphics in the Ryzen 5 5600G support gaming on Windows 11?
Yes, the Vega 7 integrated graphics in the Ryzen 5 5600G can support gaming on Windows 11, providing a cost-effective solution for casual gaming and general use on the latest operating system.
What is the boost clock speed of the Ryzen 5 5600G, and how does it enhance performance?
The boost clock speed of the Ryzen 5 5600G is typically around 4.4 GHz, allowing the processor to handle demanding tasks more efficiently, providing a performance boost especially in CPU-intensive applications.
How does DDR4 RAM compatibility affect the performance of the Ryzen 5 5600G in games?
DDR4 RAM compatibility with the Ryzen 5 5600G affects gaming performance by providing sufficient bandwidth and speed for processing game data, which, when paired with technologies like AMD’s Smart Access Memory, can enhance the overall performance in games.